Explain How the Electrochemical Gradient Differs Between Na+ and K+
Know also for this to actually work the pump needs to act in both directions. Sweat glands secrete into their lumen a fluid that is identical to interstitial fluid.
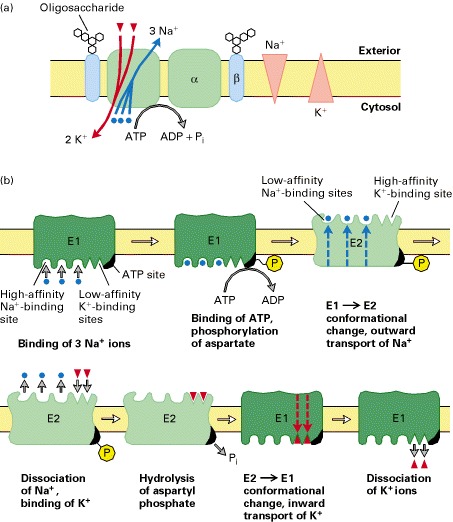
Na K Channel Pumps The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki
It is a primary active transporter.
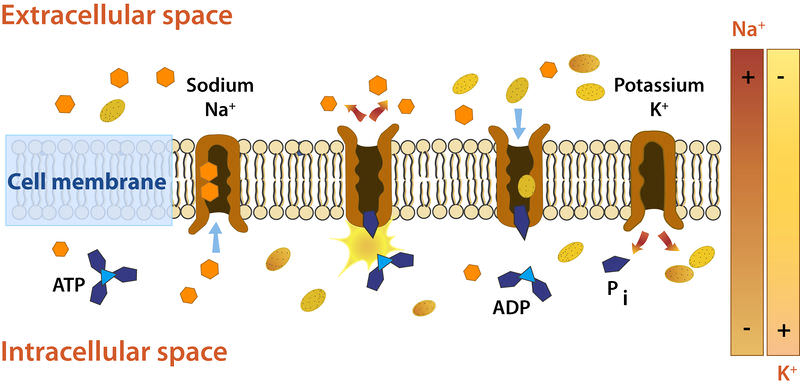
. Explain how energy from the Na and K electrochemical gradients across the plasma membrane can be used to drive the net uphill against a gradient movement of other solutes eg Naglucose co-transport. The resting membrane potential is the steady potential of unstimulated cell. To maintain this ionic gradient the cell membrane has a Na K -pump which requires a source of energy viz ATP.
1 Answer to Explain the differences between a chemical gradient an electrical gradient and an electrochemical gradient. The Electrochemical Gradient refers to the combination of the previous two gradients. The electrical gradient of K a positive ion also tends to drive it into the cell but the concentration gradient of K tends to drive K out of the cell.
NaCa2 exchange or counter-transport. Solution for The NaK pump works against the electrochemical gradient. The cell membrane is differentially permeable to K and Na being more permeable to K than to Na in the resting state.
Explain how the electrochemical gradient differs between Na and K. High concentration inside negative inside -- little to no movement. The Electrical Gradient refers to the difference of charges between substances on different sides of the Membrane.
There is a larger electrochemical gradient driving the movement of Na into the cell compared to the net force moving K out of the cell. 15 mM Extracellular ion concentration. To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient the cell must utilize energy in the form of ATP during active transport.
In the resting state the plasma membrane has slight permeability to both Na and K. Rep gems come when your posts are rated by other community members. The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer that arranged asymmetrically containing cholesterol.
Construct the same table for Na and Cl-you will want to pick different voltages. The Na - KATPase pump contributes to the membrane potential by pumping 3 Na out of the cell for every 2K taken in. Na channels open and allow influx of positive charge rapidly depolarizing the inside of the cell.
It exists because of a tiny excess of negative ions inside the cell and positive ions outside the cell. To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient a cell must use energy. Apply this principle to understand oral rehydration procedures.
An electrochemical gradient is composed of two forces. Thus there is a continuous tendency to loose K. However the permeability for K is much greater due to the presence of K leak channels embedded in the plasma membrane which allow K to diffuse out of the cell down its electrochemical gradient.
This occurs because the inward electrical force is now larger than the outward concentration gradient. This gradient moves _____ out of the cell against both gradients. So it pumps Na against the Na concentration gradientthe Na concentration is just the opposite.
The energy from the concentration gradient the force derived from the charge differential across the membrane referred to as the membrane potential. Basically the concentration gradient of Na wanting to move in the cell is opposed by a positive membrane potential of 60 mV. Positively charged and higher concentration outside cells than in cells -- enters cell K.
Here is a chloride cell in the gill epithelium of a fish. Which of the following would be true of CFTR. The Na K ATPase pumps 3 Na out of the cell and 2K that into the cell for every single ATP consumed.
Report 10 years ago. As the fluid moves through the lumen on its way to the surface of the skin the cells of the sweat. For reference NKA NaK ATPaseNKCC NaKCl- cotransporter.
Th e nervous tissue consists of excitable c ells neurons which can g enerate action potentials. Active transport mechanisms do just this expending energy often in the form of ATP to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells. Low inside the cell and high outside.
On the cytosolic side. The Na K pump is an electrogenic transmembrane ATPase first discovered in 1957 and situated in the outer plasma membrane of the cells. Really simply put the concentration of 3Nas out and 2Ks is maintained by the sodium-potassium pump - this requires ATP and anything associated with active transport usually means against the concentration gradient from low to high.
At -100 mV the net flow of K will be IN. Moving against a gradient. Therefore at -12 mV the net flow of K will still be OUT.
NA is 145 extracellular and 15 intracellular. By utilizing the energy contained by ATP it pumps K against the concentration gradientthis is an energy dependent process. They have different voltages between the inside and outside of it.
The electrical and concentration gradients of a membrane tend to drive sodium into and potassium out of the cell and active transport works against these gradients. CFTR allows for movement of Cl- from inside the cell out into the water down a concentration gradient. As the concentration of Na ions increases in the cell the electrochemical gradient decreases and voltage gated Na channels begin to Deactivate K voltage gated channels sense a positive potential charge they open and allow a rush of K ions out of the cell bringing the net charge.
It usually ranges between -50 to -75MmV. It is a symporter. The combined gradient of concentration and electrical charge that affects an ion is called its electrochemical gradient.
Explain the differen ce between a chem ical and elect rochemical gradient chemical i s the concentration gradient elect rochemical is con centration-dependent an d charge-dependen t.

Structure And Regulation Of Na K Atpase Na K Atpase Is A Download Scientific Diagram

Post Albers Diagram Of The Na K Transport Cycle In This Simplified Download Scientific Diagram

Diagrammatic Representation Of The Transport Of Na 3 And K 2 By Nka Download Scientific Diagram

The Electrochemical Gradient Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
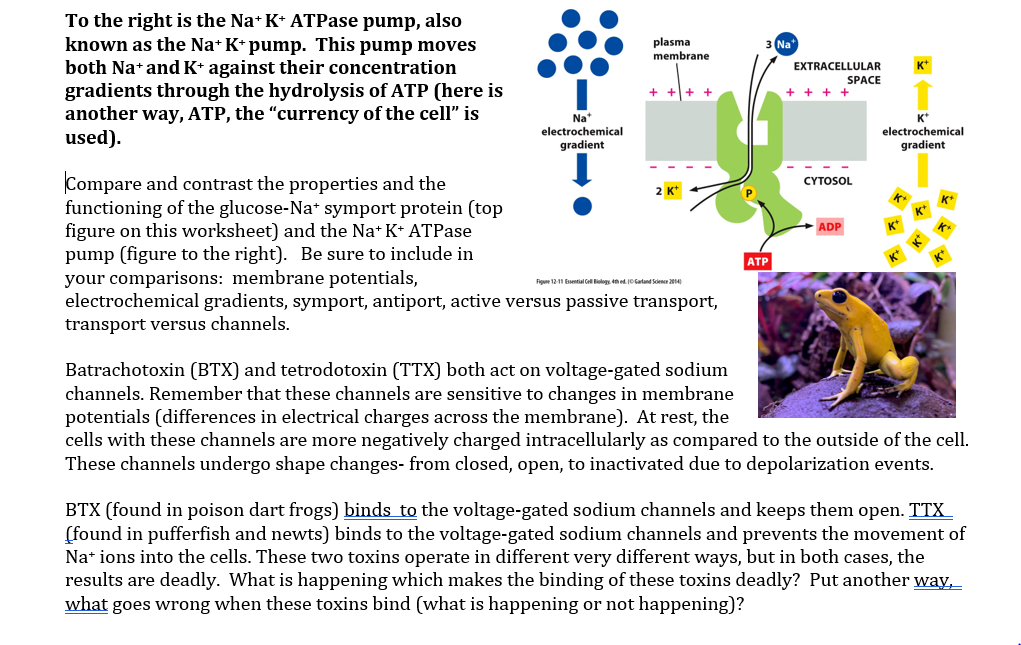
Solved The Glucose Na Symport Protein Uses Chegg Com

Cv Physiology Na Sup Sup K Sup Sup Atpase

2 15 Sodium Potassium Pump K12 Libretexts
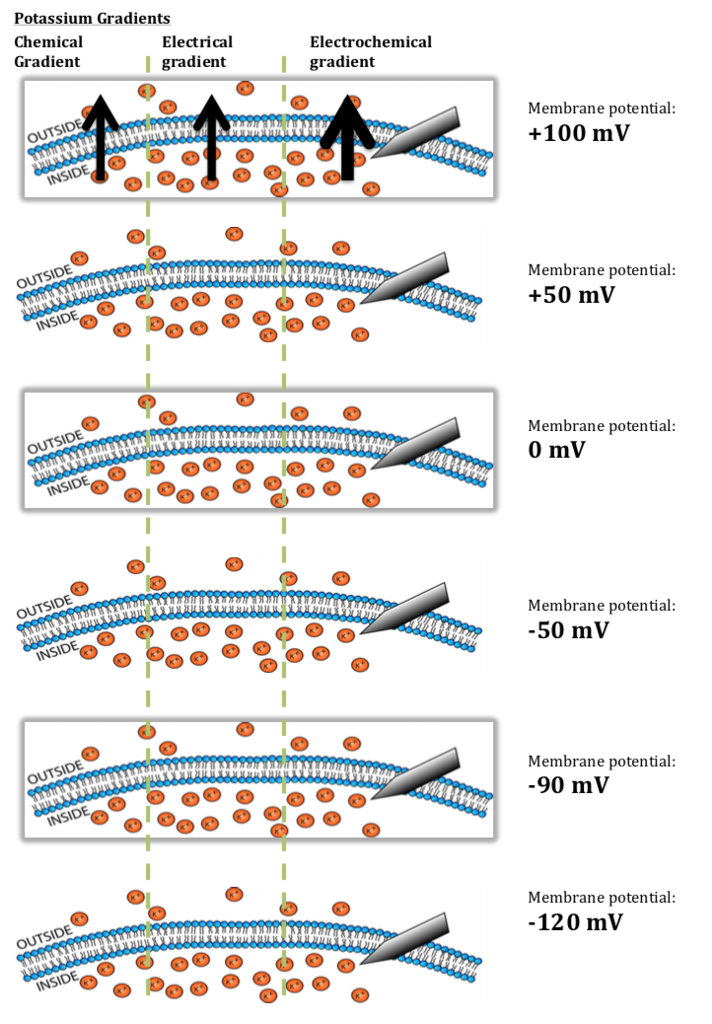
Solved The Next Questions Show A Cell Membrane With Either Chegg Com

The Membrane At Rest Foundations Of Neuroscience

Sodium Potassium Pump Ck 12 Foundation

The Na K Atpase Reaction Cycle The Sequence Of Steps Involved In The Download Scientific Diagram

4 15 Na K Pump Make Flash Cards Biochemistry Notes Plasma Membrane

Active Transport Boundless Biology
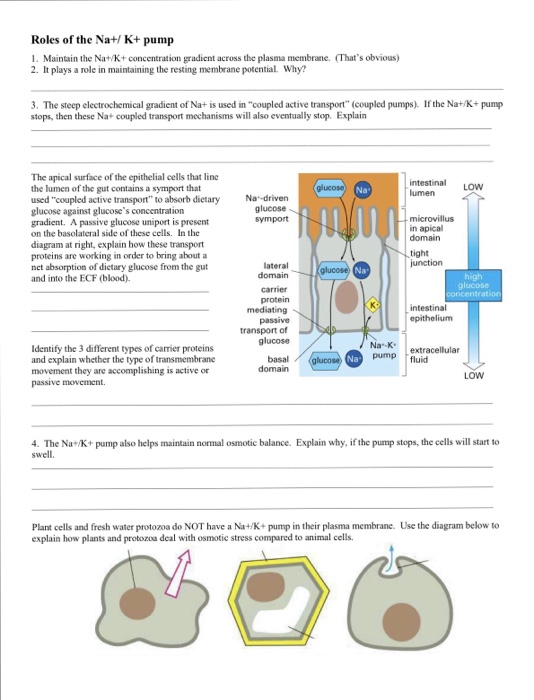
Solved Roles Of The Na K Pump 1 Maintain The Nat K Chegg Com

How Does Na Get Inside The Cell Quora

Biochemistry If Concentration Of K Ions Inside The Cell Is Almost Equal To Concentration Of Na Ions Outside Of The Cell Why These Ions Cross The Membrane Chemistry Stack Exchange

Comments
Post a Comment